Software
This page lists several publicly-available software items that I have (co-)developed in the past.
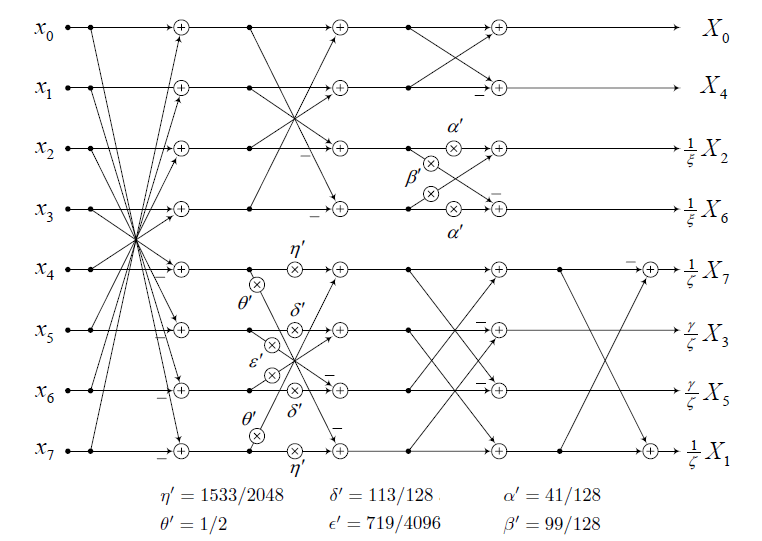
MPEG integer IDCT standard (ISO/IEC 23002-2)
This is a reference implementation of MPEG's standard for integer approximations of 8x8 DCT/IDCT (Discrete Cosine / Inverse Discrete Cosine Transforms). DCT/IDCT are fundamental operations used in most existing image and video coding standards (including JPEG, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 p2, H.261, and H.263), and encoder/decoder implementations using this MPEG standard are guaranteed to be drift-free and passing all relevant IDCT precision tests and conformance requirements. Detailed description of the algorithm can be found in:
- Y. A. Reznik, A. T. Hinds, L. Yu, Z. Ni, and C-X. Zhang, "Efficient fixed-point approximations of the 8x8 inverse discrete cosine transform" (invited paper), Proc. SPIE Vol. 6696, Sep. 24, 2007. (pdf)
.
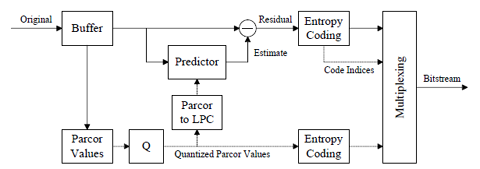
MPEG-4 ALS: Lossless Audio coding standard (ISO/IEC 14496-3:2009 / 11)
MPEG-4 ALS is a standard for lossless audio coding, developed in 2003-2005 timeframe. It is a linear predictor (LPC)-based waveform coder, transmitting filter coefficients and residual in a manner that allows lossless reconstruction. General description and latest reference software for this standard can be found at TU-Berlin website.
My contributions to this standard included algorithms for quantization and coding of Parcor coefficients, coding of residual, and parts of block-switching and multiplexing logic. Detailed description of residual coding can be found in:
- Y. A. Reznik, "Coding of Prediction Residual in MPEG Standard for Lossless Audio Coding", Proc. IEEE Intl. Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2004), Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2004, pp. 1034--1038. (pdf)
- T. Liebchen and Y. A. Reznik, "Improved Forward-Adaptive Prediction for MPEG-4 Audio Lossless Coding", Proc. 118th AES Convention, Barcelona, Spain, May 28-31, 2005. (pdf)
This is an implementation of a "type coding" algorithm from:
- V. Chandrasekhar, Y. Reznik, G. Takacs, D. M. Chen, S. S. Tsai, R. Grzeszczuk and B. Girod, "Quantization Schemes for the Compressed Histogram of Gradients descriptor," Proc. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'10), pp. 33-40, San Francisco, CA, June 2010. (pdf)
This algorithm receives simplex-constrained quantities, such as discrete probability distributions, and quantizes them to a set of points known as "types" in universal source coding literature. Plots below show type locations and corresponding Voronoi partitions in 3 dimensions.
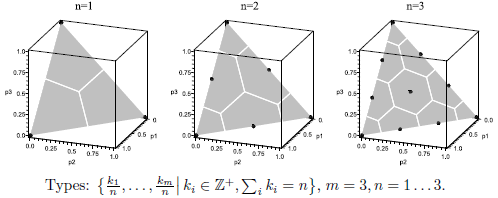
Detailed description and analysis of performance of this algorithm can be found in:
- Y. A. Reznik, "An Algorithm for Quantization of Discrete Probability Distributions," Proc. Data Compression Conference (DCC'11), pp. 333-343, Snowbird, UT, March 2011. (pdf)
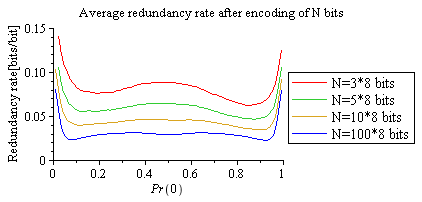
This library implements a simple binary adaptive encoder described in:
- Y. A. Reznik, "Practical Binary Adaptive Block Coder", Proc. Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, April 2007. (pdf)
This algorithm encodes data in small (e.g. 8-bits) blocks, and uses a stack of prior blocks for adaptation to source's statistics. In practice, if bits are coming one-by-one, there will be a need to accumulate them, but the benefit of doing so is much faster encoding and decoding. Only a couple of lookups and logic operations are needed to encode each block. This algorithm is significantly faster than binary arithmetic encoders (including H.264's CABAC, and JPEG's Q-Coder). Plots below show redundancy rate characteristics of this particular implementation.